Have you ever heard that people remember only 20% of what they read but 80% of what they see? While the exact percentages are debatable, the basic idea isn’t: It’s easy for people to learn and process information visually.

That’s why most websites use images, and why it’s important to include images on your own That’s why most websites use images and why it’s essential to include images on your site. Pictures help make your content more informative, engaging, and memorable. In addition to improving the visitor experience, they can also help boost your organic search traffic.
If you use a website-building platform like CMS Hub or WordPress, just click the image icon in your toolbar, select an image from your file manager, and insert it. If you don’t use a builder, you can still easily add images to your website. You just need to know some HTML. Let’s walk through the process below.
How to Insert an Image in HTML
To insert an image in HTML, use the image tag and include a source and alt attribute. Like any other HTML element, you’ll add images to the body section of your HTML file.
The syntax looks like this: <img src=“URL” alt=“descriptive text”>
The HTML image element is an “empty element,” meaning it does not have a closing tag. Unlike elements like paragraphs that consist of an opening and a closing tag with content in between, an image specifies its content with attributes in the opening tag.
Compare the following lines of code to see the difference between a paragraph and an image:
Notice the two attributes in the image element above, src and alt. Let's discuss both of these important attributes next. This video dives deeper into the steps we just explained:
The img src Attribute
An image element must always have a src (source) attribute containing the image URL or file path. Otherwise, the browser will not know what to render. Permitted image file types will depend on the browser that loads the page, but all browsers allow you to place standard formats like .jpeg, .png, and .gif, as well as .svg.
In the code example above, the source is a full hyperlink because the image is being fetched from another website. If you want to place an image stored on your server, you can use the image file path without the website name or protocol.
For example, if the image is located in a subfolder stored in the same place as your HTML file, your image element can look more like this:
In this case, “csz” would be a folder located in the same directory as your HTML file.
The img alt Attribute
While a browser can render an image without the alt attribute, including this attribute is considered a best practice. That’s because this attribute contains image alt text.
Image alt text is important for a few reasons. First, it will appear in place of an image if the image fails to load on a user’s screen. Second, it helps screen-reading tools describe images to readers with visual impairments who might have trouble understanding the image without it.
Third, image alt text allows search engines to better crawl and rank your website. Google Images — not Google Search, Google Image Search — is a major search engine on its own, and another way people can find your website.
Providing images with descriptive alt text can help you rank for your target keywords and drive traffic to your site. In 2019, HubSpot did exactly that, leading to a 25% year-over-year growth in organic traffic that came from web and image searches.
The img style Attribute
You might also see a style attribute inside an <img> tag containing the width and height of the image. Specifying the width and height can help prevent the web page from flickering while the image loads. Here’s how the code might look with these additional attributes:

It’s important to note that you can also specify the size of an image using internal or external CSS, over inline CSS. To learn the difference between these three types of CSS, see our guide on adding CSS to HTML.
The img width and height Attributes
The width and height of an image can also be specified in pixels with separate width and height attributes, like so:
This will produce the same result as the image above, where the style attribute was used.
The main difference between these methods is that using separate width and style attributes will tell the browser how much space to save for the image, which may result in smoother loading (though this will depend on your page layout, ultimately).
How to Insert a Background Image in HTML
If you’d like to set an image as the background of a web page or an HTML element, rather than simply inserting the image onto the page, you’ll need to use the CSS background-image property.
This CSS property replaced the background-image attribute in previous versions of HTML. It’s much more flexible and predictable than the HTML attribute — and still easy to use.
To set the value of background-image, you have to use the following syntax:
url(‘ ’);
Between the single quotation marks, you’ll put the image URL or file path.
How to Insert a Background Image on a Page
To start, let’s say you want to set an image as the entire page's background. In this case, you would apply CSS to the body element. Using a CSS selector, you can define the background-image property in the head section of your HTML file or an external stylesheet.
For this demo, we’ll use the same image as above and change the text color to white so we can see it.
Here’s the HTML and CSS.
Here’s the result:

Looks great! But what happens if the image is smaller than the browser? In that case, it will display multiple tiles, as shown below.
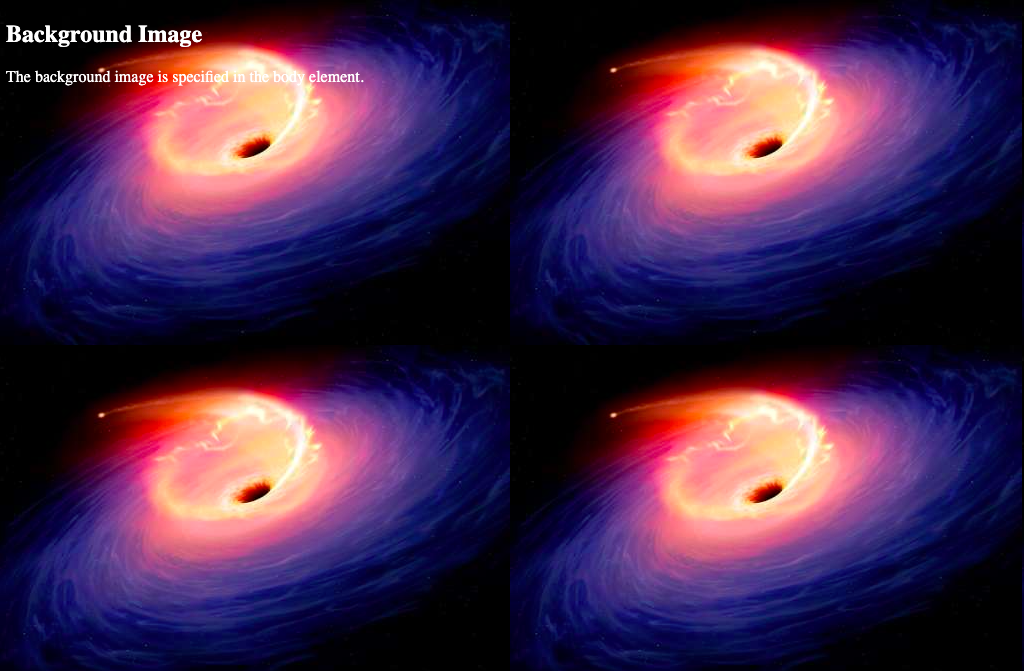
To prevent this from happening, you can use the background-repeat property and set it to no-repeat.
Here’s the CSS.
The HTML stays the same. Here’s how it would look on the front end now.
You’ve solved the repeating problem, but now you have a lot of extra whitespace below and to the right of the image. To ensure the background image covers the entire body element — or, in other words, takes up the entire browser window — you can use the background-size property and set it to cover.
Then, to prevent the image from warping its dimensions, use the background-attachment property and set it to fixed. That way, the image will keep its original proportions.
Here’s the CSS.
The HTML stays the same. Here's how it would look on the front end now.

How to Insert a Background Image on an HTML Element
You can also set an image as the background of an HTML element rather than the entire web page.
For example, you could place HTML elements inside a div, then target the div with the CSS properties we used above. One difference is that instead of setting the background-size property to cover, we’re going to set it to 100% 100%.
That means the image will stretch horizontally and vertically as needed to fit the entire div element, without retaining its original dimensions.
Here’s the CSS and HTML.
Here’s the result.

How to Make an Image Link in HTML
Images are also effective links — you can link an icon or a high-res image. Either way, the process is the same: Enclose your <img> element in an <a> (anchor) tag, like so.
Here’s an interactive example — click the HubSpot logo to be taken to the HubSpot homepage.
See the Pen Create an Image Link by HubSpot (@hubspot) on CodePen.
Making Your Website Visual
Adding images to your website is important to your visitor experience and search engines. Whether you‘re building your website with a content management system or from scratch, it’s easy. You just need to know some HTML and CSS. Add images to your website today!
Editor's note: This post was originally published in September 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.




![HTML Projects for Beginners: How to Create a Personal Portfolio Page [Step-by-Step]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/personal_portfolio.png)